
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/command-window-ping-responsive_ip-5806b40f3df78cbc2845ab91-5a982255ae9ab8003783f221.png)
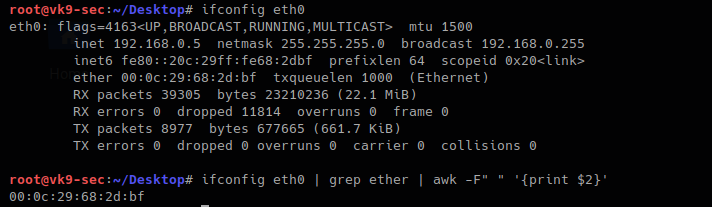
This option tells Nmap not to do a port scan after host discovery, and only print out the available hosts that responded to the scan. Here is a little quote from the man page, nmap(1): -sn (No port scan) Network ID is 192.168.3.0, just substitute the last number by 0. Here at point 2, I have the wlan0 device. Inet6 fe80::c685:8ff:fe94:ee9a/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever Inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverĢ: wlan0: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000 Please substitute your network identifier and subnet mask.ġ: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN The part next to the Ethernet adapter using the current IP address, denoted as HWaddr, is your MAC address.You can use the Nmap utility for this.Type gnome-terminal for Gnome desktop environment, konsole for KDE desktop environment and click "Run".From the desktop, open the "Run Application" window using the Alt+F2 key combination.The twelve-digit character strings labeled Physical Address in the list are the Mac addresses of the network adapters connected to the computer.
In the command prompt window, type getmac and press Enter. The second way to find out the Mac address is to run the "getmac" command. The twelve-digit string labeled Physical Address under the ethernet adapter is the MAC address of that adapter.Ģ. This command will list the network adapters (wireless, local network connection, etc.) on the computer. Type ipconfig /all or ipconfig -all and press Enter.
In the command prompt window that opens, the mac address can be learned in 2 ways ġ. Press Start, type "cmd" when the screen opens, or type "run" and enter when Start is open, type "cmd" in the box that appears, and enter the "command prompt" application.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
